However. sometimes these data might get corrupted which in turn could result in negative consequences on the entire app ecosystem. Along the same lines, if a lot of temporary data gets accumulated over the due course of time, then it could slow down the associated app. This is the reason why it is always recommended to delete these data at regular intervals. And in this guide, we will show you how to do just that, via five different methods. So without further ado, let’s get started with the steps to delete the cache files on Android devices.
How to Delete Cache in Android via ADB, Fastboot, Recovery
The five different methods discussed here are: via the Settings menu, using ADB Commands, via Fastboot Commands, from Stock Recovery, and using a custom recovery like TWRP. We have discussed the best-case scenario for each of these methods under their respective sections. So go through them and then decide which one is in sync with your requirement.
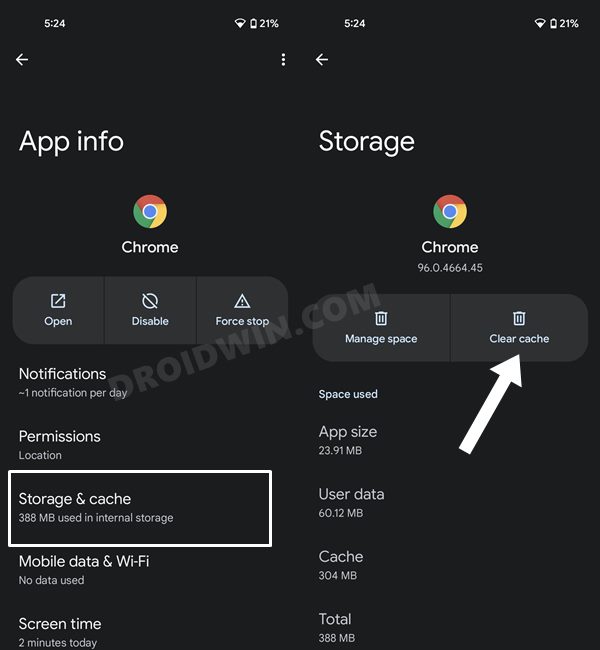
METHOD 1: Delete Cache from Settings
This method is best suited when you are planning to delete the cache of a few apps. And is usually recommended when the app isn’t performing along the expected lines. So with that in mind, follow the below steps to delete cache on your Android device via the Settings menu.
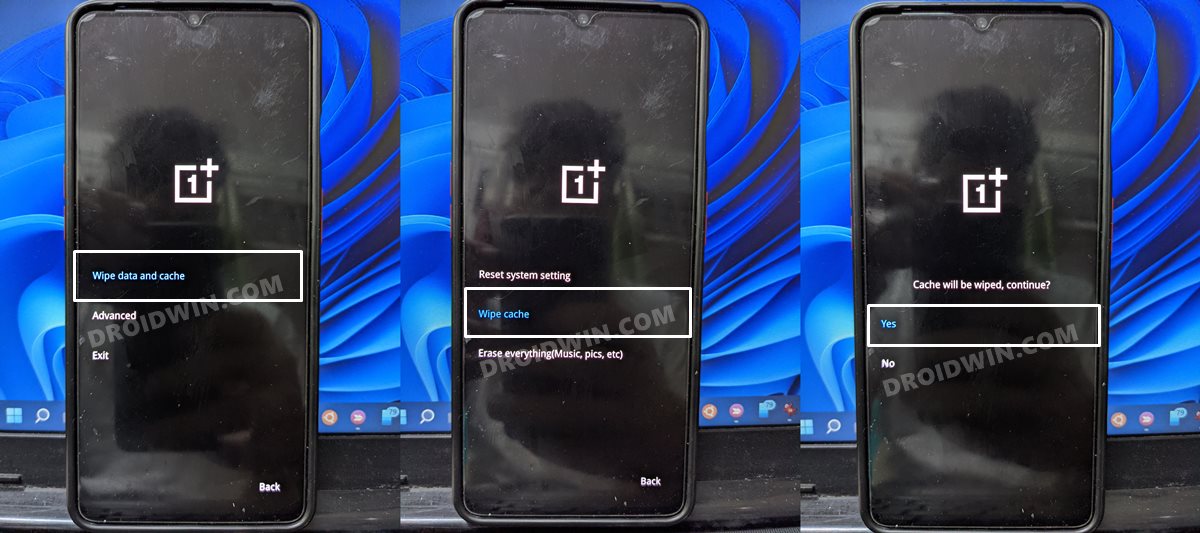
METHOD 2: Delete Cache via Stock Recovery
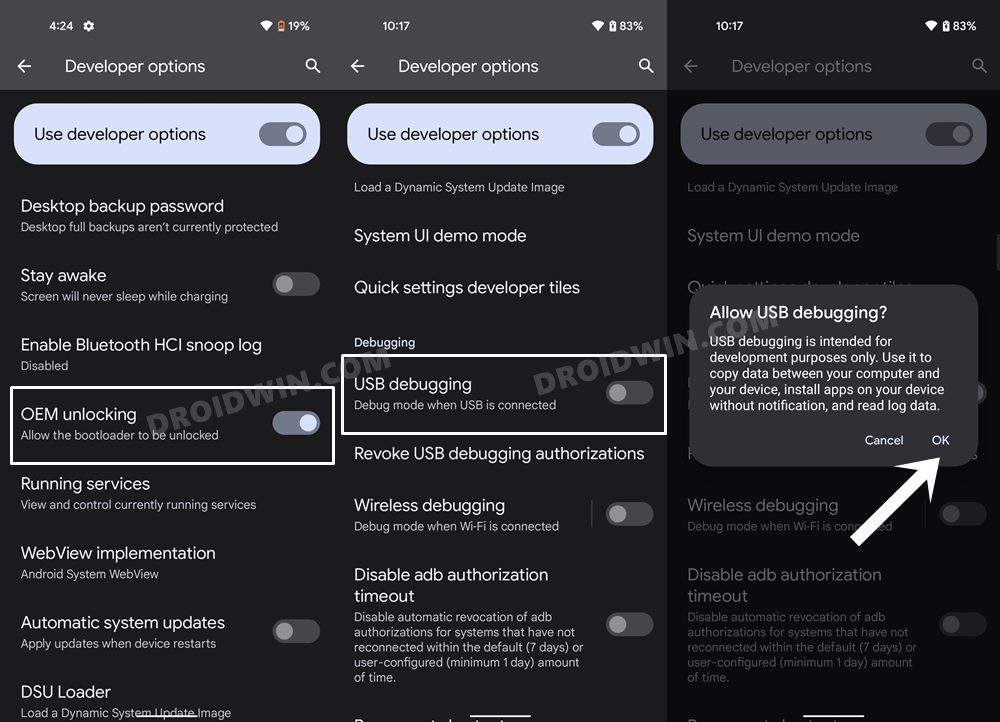
If you want to delete the cache data for numerous apps, then manually carrying out that task for each of those apps would take ages. Likewise, if you are planning to delete the cached data for the system process, then you wouldn’t be able to do so from the Settings menu. In both these cases, you will have to take the help of the stock recovery to delete the cache files from your Android device. In this regard, different devices have different key combinations when it comes to booting the device to stock recovery. Therefore, to avoid any confusion, we will instead be listing out the universal ADB method that is applicable across all the devices. Follow along.
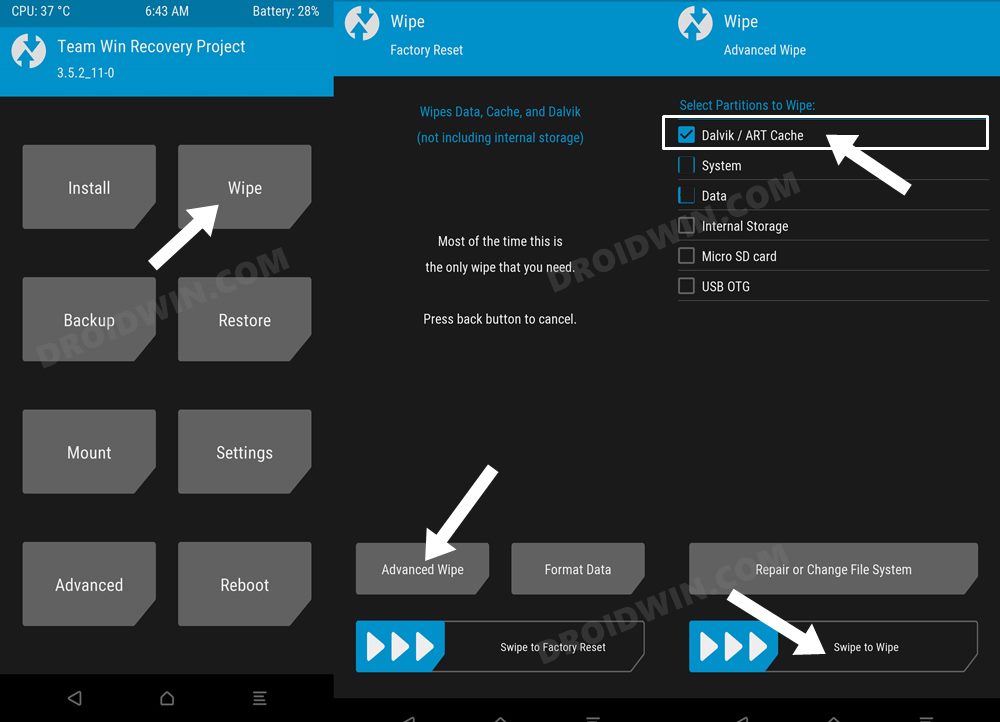
METHOD 3: Delete Cache via TWRP
If you are dealing with custom binaries, ROMs, and firmware, then you might be having a custom recovery like TWRP installed as well. So let’s use that custom recovery to delete the cache files from your Android device.
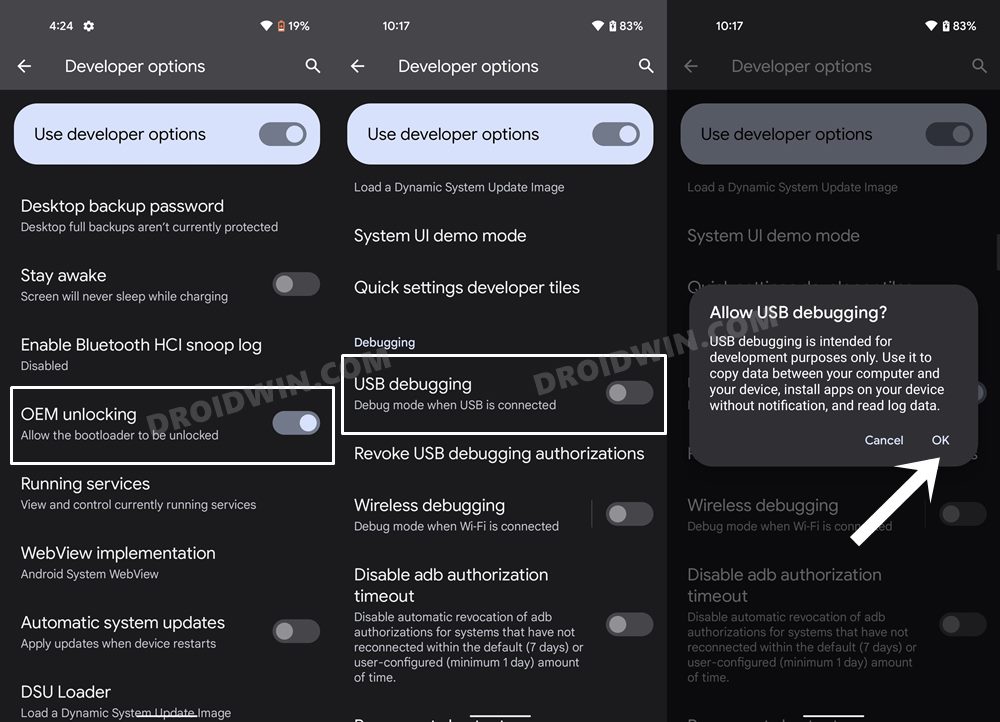
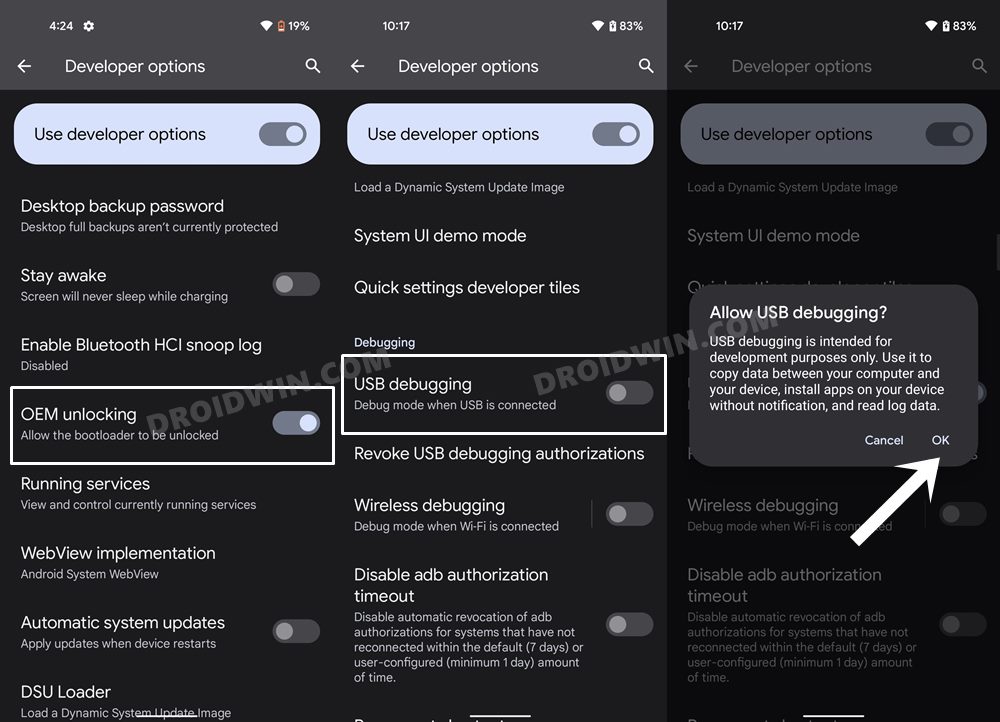
METHOD 4: Delete Cache via ADB Command
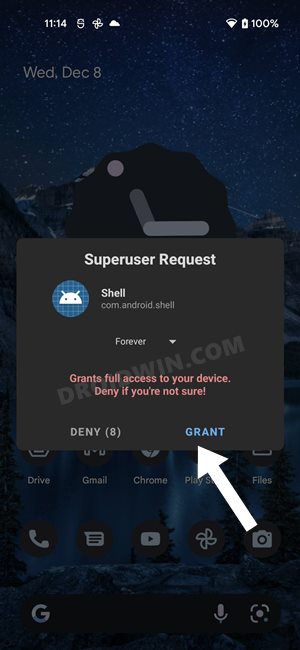
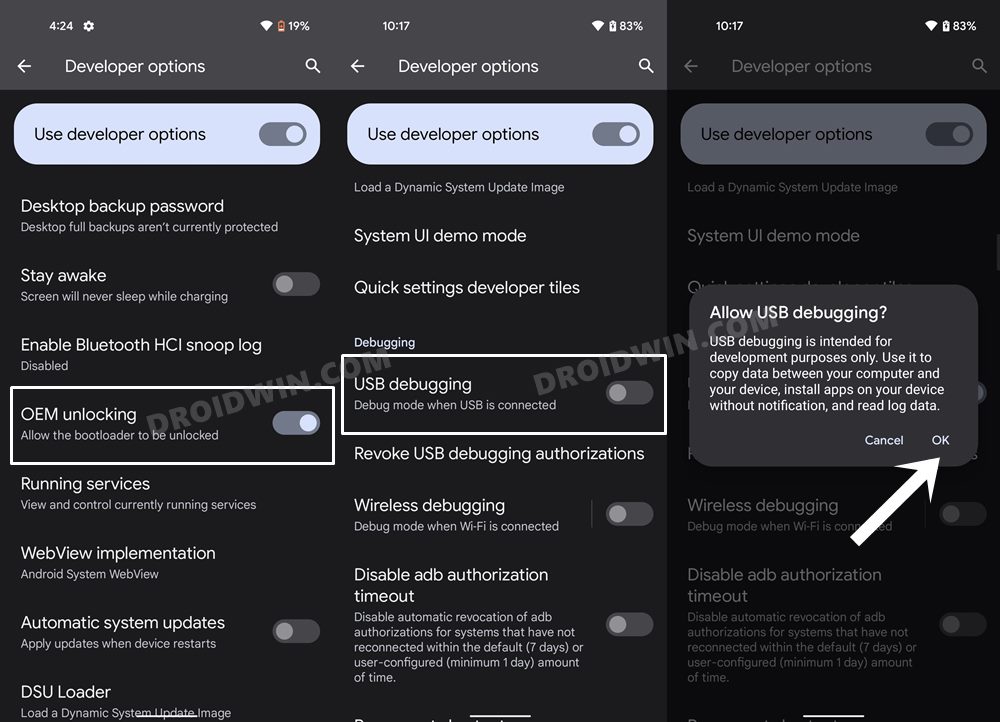
For this process to work, you will need to have administrative-level privileges, in other words, your device should be rooted. If that’s well and good, then proceed ahead with the below steps. However, if your device isn’t rooted, then just doing so for the sake of deleting cache might not be the most feasible approach as rooting might void the warranty and would lead to factory reset. (Actually, unlocking the bootloader results in both these consequences and not rooting. But since unlocking the bootloader is the first step for rooting, your device will have to suffer both these consequences one way or the other). Therefore, it’s better to avoid these issues and you should instead opt for the first three methods that we have listed above in order to delete cache from your Android device.
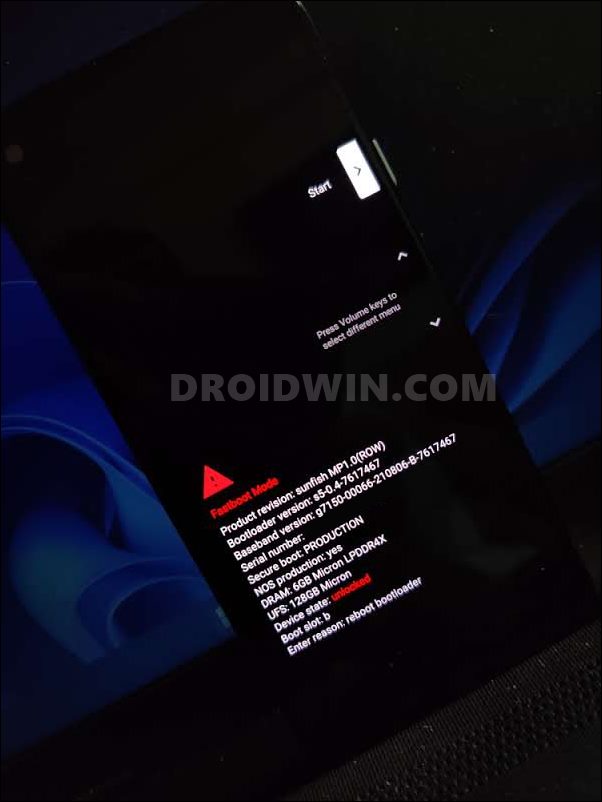
METHOD 5: Delete Cache via Fastboot Commands
While this method of deleting cached doesn’t require system-level access or root, but its efficiency rate is somewhat debatable. While it spelled out success for some of the users, for others, it lead to access denied error. Well, if you are a tech enthusiast and are willing to take the risk, then let’s get started: So with this, we round off the guide on how you could delete cache from your Android device. We have listed five different methods for the same, spread across varied domains. If you have any queries concerning the aforementioned steps, do let us know in the comments. We will get back to you with a solution at the earliest.
What is Android 12L? How to Install Android 12L?WiFi not working in Android 12: How to Fix [12 Methods]Bluetooth Not Working in Android 12: How to FixHow To Enable Two Button Navigation in Android 12
About Chief Editor