However, many users are now questioning their decision whether or not they should have made a switch from Chrome to Edge. This is because the latter isn’t proving to be any good either. Various users have voiced their concern that the Edge browser is performing extremely slow and sluggishly on the latest OS build. The browser takes ages to open, the tabs are taking forever to load a page, and in some instances, the webpage ends up displaying an Out of Memory error.
The efforts the Redmond giants have put in forcing this browser onto its userbase are quite commendable. However, if they would have put at least a fraction of this effort towards improving the browser’s performance as well, then it would made the browsing experience much easier and streamlined. Anyways, there are still some silver linings among those dark clouds so let’s keep our focus on them. So in this guide, we will list out numerous methods to fix the slow and laggy performance of Microsoft Edge in Windows 11.
How to Fix Microsoft Edge Slow or Laggy in Windows 11
Do note that there’s no universal fix as such. You will have to try out each of the below-mentioned workarounds and see which one works best in your favor. So with that in mind, let’s get started.
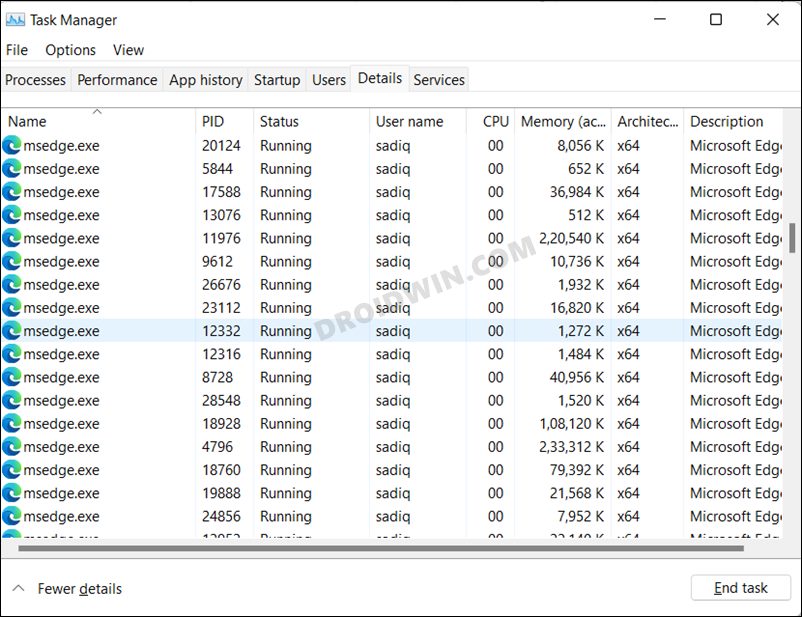
FIX 1: Restart Edge Processes
Your first course of action should be to restart Edge and all its processes. Doing so will give it a fresh instance to work upon and this, in turn, might rectify the underlying issue as well. So refer to the below instruction steps to try it out:
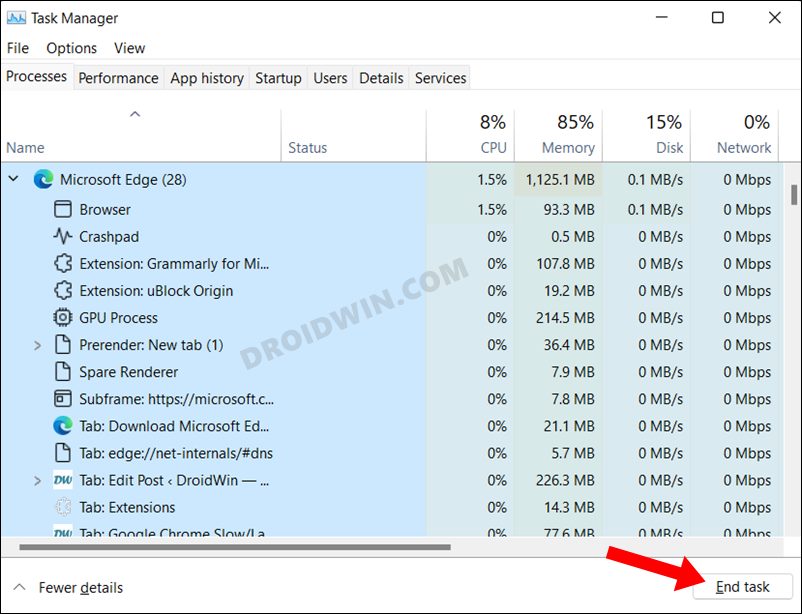
FIX 2: Restart Services via Edge Task Manager
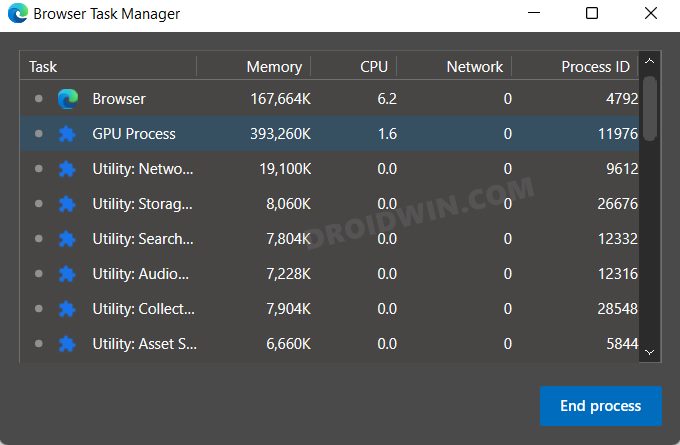
Edge (and other Chromium browsers too) comes with a built-in Task Manager that lists out all the running browser services and processes as well as the total CPU and RAM they are consuming. With the help of this data, we will be able to get hold of those services that are consuming more than the permissible level of system resource, and we will then disable those services. So proceed with the below steps to try it out:
FIX 3: Disable Preload Pages in Edge
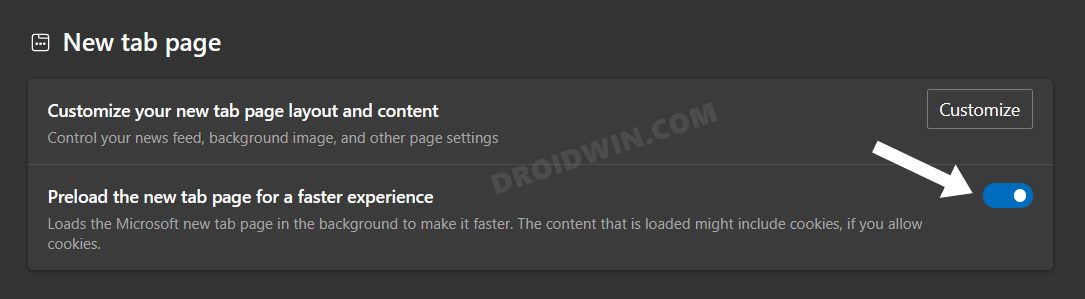
Edge automatically preloads a few web pages that it thinks you might visit at a later date. It does so based on the cookies that it had collected and based on your browsing history. However, this feature has more drawbacks than benefits as it ends up consuming necessary storage space as well as crucial system resources, with the only benefit being that you would be able to view these pages a few seconds earlier. So with the caveats outweighing the perks, it’s better to keep this feature disabled, which could be done as follows:
FIX 4: Disable Secure DNS
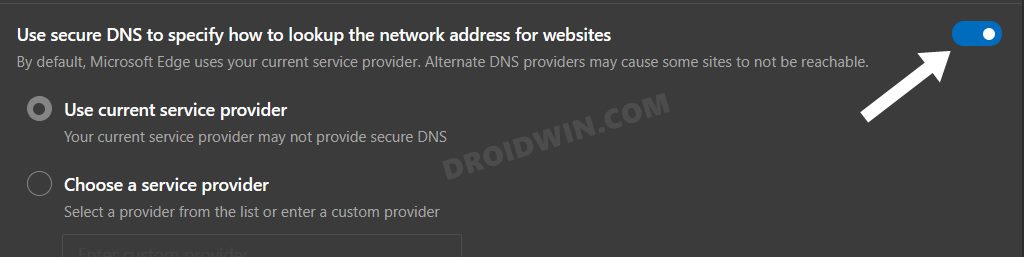
Various users have reported that when the browser uses a secure gateway to the Domain Name Server, then it ends up taking a considerable amount of additional time frame. Therefore, you could consider disabling it, using the instructions listed below:
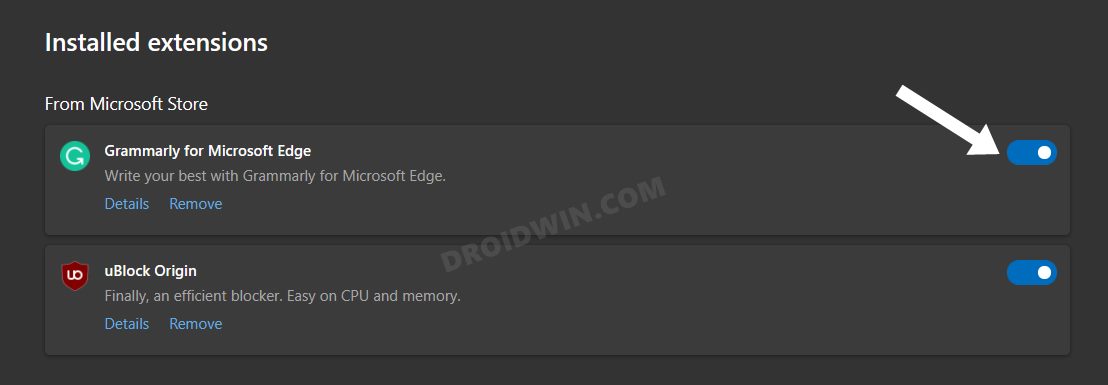
FIX 5: Disable Edge Extensions
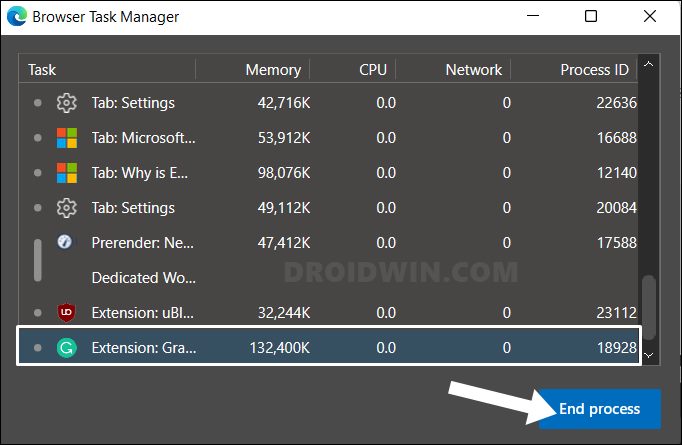
It’s no hidden secret that extensions contribute a lot towards memory consumption. One major reason for that is the fact that these add-ons are continuously running in the background while you are working inside the browser environment in the foreground. So you could consider temporarily disabling these extensions and let the browser cool down a little bit. Once a considerable time period has elapsed and Edge is running along the expected lines, you may then re-enable the disabled extensions. However, if the extensions shoot up the memory resources every time you enable them, then it’s better to remove it from the browser and look out for their alternatives. Here’s how all of this could be carried out:
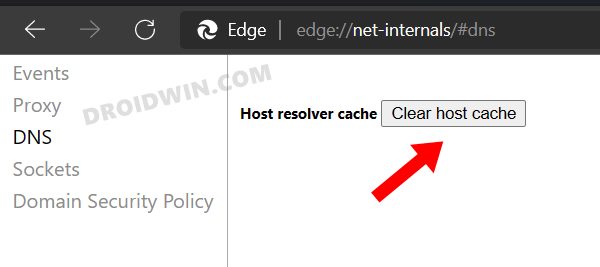
FIX 6: Flush Edge DNS
Edge stores the data related to the websites you visit in its Domain Name Server. But if a lot of data gets stored in this record book, then it could slow down the loading of the websites as well have negative consequences on the browser as well. Therefore, consider deleting these data and let the browser repopulate them from scratch the next time you visit that site.
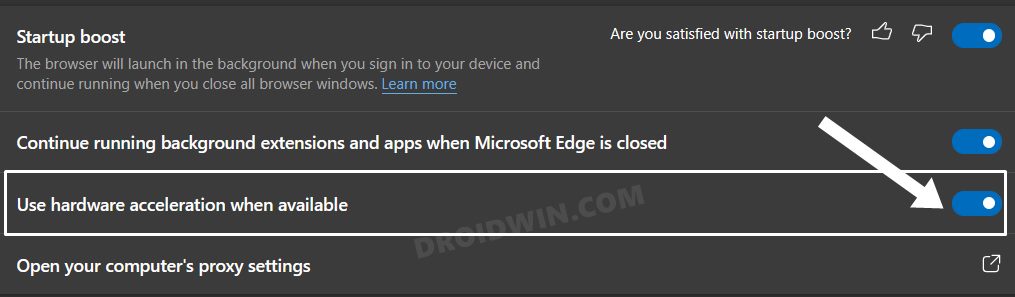
FIX 7: Disable Edge Hardware Acceleration
The Hardware Acceleration feature checks the prowess of your PC’s CPU as well as GPU and if it finds the latter’s processing capability to be much more than the formers, then it allocates the browser’s functionality to the latter aka GPU. But it is still a debatable topic as to how GPU could eclipse the CPU in this aspect, and hence the general advice is to disable this feature. Here’s how it could be done:
FIX 8: Opt for Edge Balance Tracking Protection
Edge comes with three different levels of tracking protection: Basic, Balanced, and Strict. And there are no brownie points in guessing which out of the three is applies the most restrictive approach. However, applying this Strict measure has its own downsides as well as it tends to be over-protective in some aspects and could in turn conflict with the proper functioning of the browser. Therefore, you should instead opt for a balanced approach, thereby maintaining an equilibrium between security and performance.
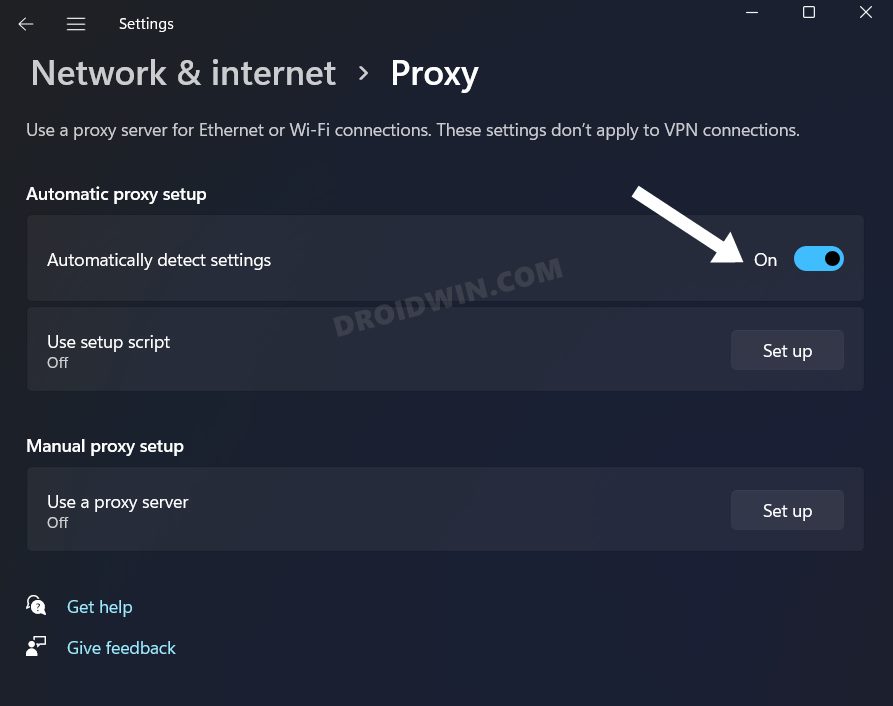
FIX 9: Disable Edge Automatic Proxy
If you have enabled Proxy on your PC to circumvent your ISP default DNS or simply to access geo-restricted contents, then it could conflict with the proper functioning of the browser. Therefore, you should disable this automated proxy setting on your PC, right from the Edge menu itself. Here’s how:
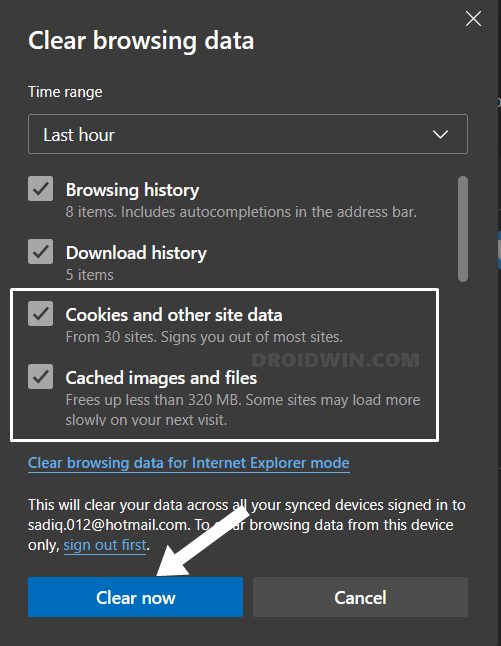
FIX 10: Delete Edge Data
If a lot of browser data gets accumulated over the due course of time or if the stored data gets corrupted, then it could spell trouble for the entire functioning of the browser. Therefore, you should consider deleting the cookie’s data as well as its cached files. So refer to the below instruction steps to try it out:
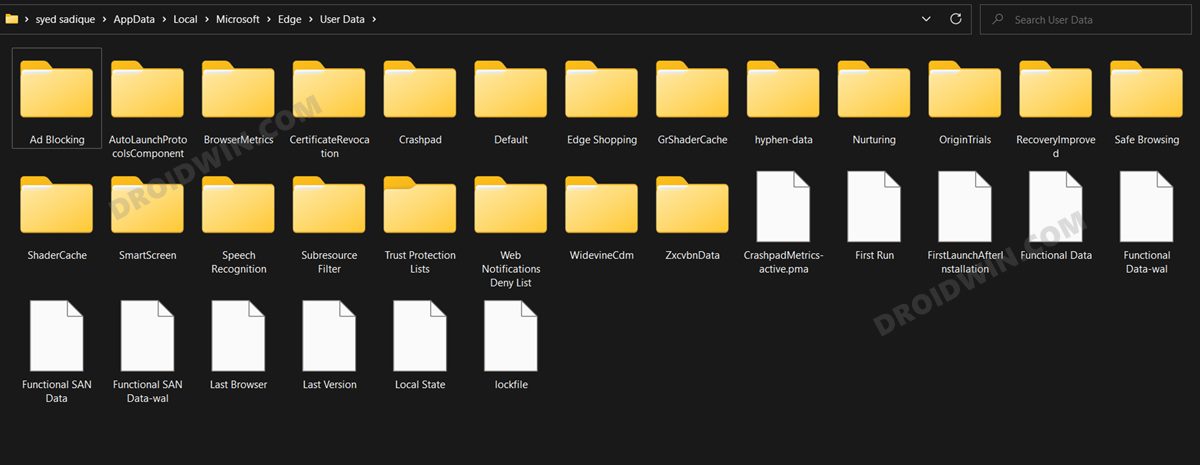
FIX 11: Delete Edge User Profile
Edge stores all the browser-related data inside the C Drive. If any of this data gets corrupted, then its repercussions will have to be faced by the entire browser environment. Therefore, you should consider deleting this Profile data and then let Edge re-populate it from scratch from your signed-in account. Do note that this will delete bookmarks, favorites, site settings, cookies, and all the locally saved data (which you could easily get back after signing in with your account).
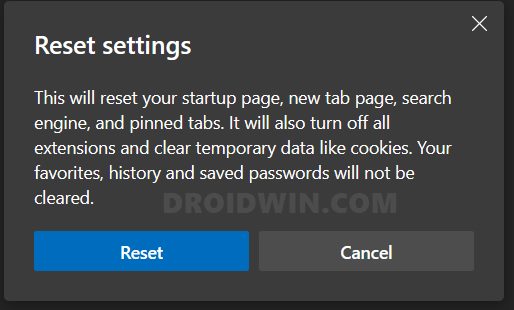
FIX 12: Reset Microsoft Edge
If the browser settings and configuration files get corrupted, then the best course of action is to reset the browser to its factory default state, exactly how it was when you first downloaded it. This will remove all the customizations and will revert it back to its original state. So proceed with the below steps and give it a try
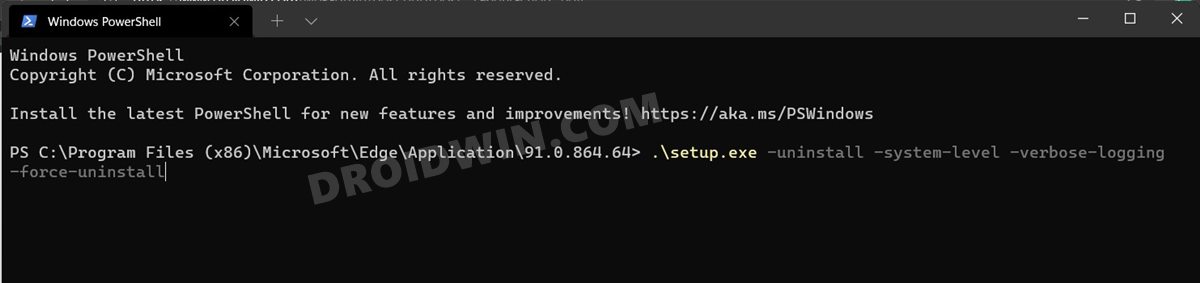
FIX 13: Reinstall Microsoft Edge
If none of the aforementioned methods worked out in your favor, then you have no choice but to uninstall and remove all the browser files from your PC and then install its fresh build. Doing so generally resolves all the browser-related issues and there is every chance that it would rectify the current issue as well. However, since Microsoft treats it as a system app (well, kind of), you wouldn’t be able to uninstall it the normal way (aka from Control Panel/Settings menu). For that, you will have to instead make use of the Powershell window. So with this, we round off the guide on how you could fix the Microsoft Edge slow or laggy performance in Windows 11. We have listed thirteen different methods for the same. Do let us know in the comments section which one spelled out success for you. Likewise, all your queries are welcomed in the comments section below.
Microsoft Edge Not Working in Windows 11: How to Fix [10+ Methods]How to Bring Back the Old Download Menu in Microsoft EdgeEnable Hidden Performance Mode/Efficiency Mode in EdgeDisable Context Menu while selecting texts in Microsoft EdgeHow to Disable Edge’s New URL Copy and Paste Feature
About Chief Editor


![]()